What Is an Overflow Valve Block and How Does It Work?
An Overflow Valve Block is a crucial component in hydraulic systems. It regulates pressure and ensures safe operation. Gordon Wright, an industry expert, once stated, "Effective pressure control is vital for machinery longevity." This highlights the importance of understanding how the Overflow Valve Block functions.
Typically housed within hydraulic systems, the Overflow Valve Block plays a significant role. It prevents pressure build-up that could lead to catastrophic failures. Improperly functioning valves can escalate risks, potentially causing irreversible damage. Understanding their mechanics is essential for maintenance and safety.
Many often overlook the significance of the Overflow Valve Block. Yet, its role is fundamental in preventing pressure overload. This can lead to system failures, which are costly and dangerous. Scrutinizing these components requires attention to detail. Regular checks and balances ensure everything operates smoothly, avoiding unexpected breakdowns.
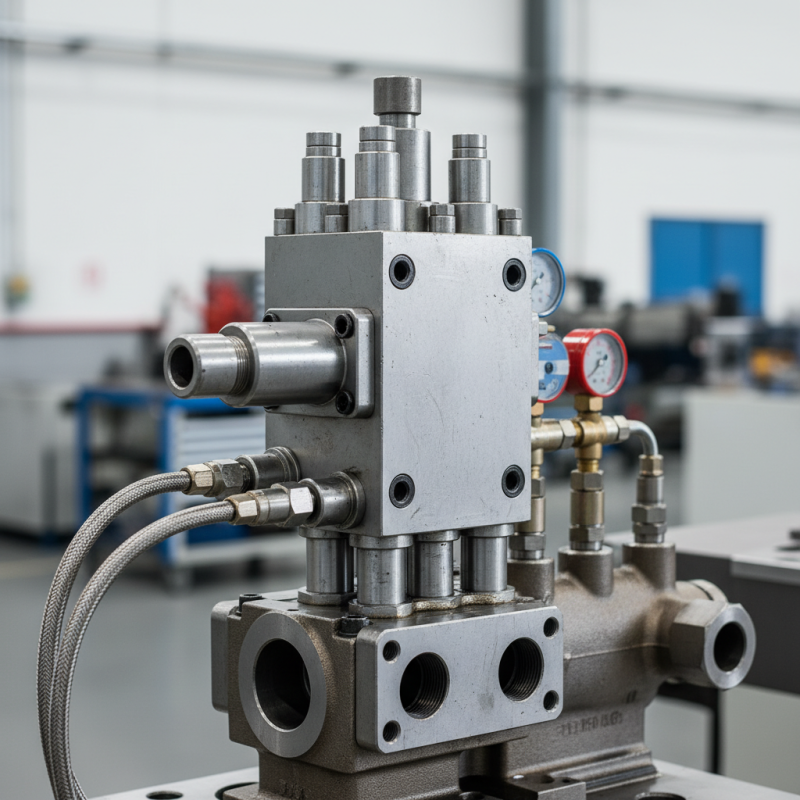
What Is an Overflow Valve Block?
An overflow valve block is a crucial component in hydraulic systems. It serves to manage excess pressure by diverting fluid. This prevents damage to machinery and keeps systems running smoothly. When pressure exceeds a preset limit, the valve opens, allowing fluid to bypass or flow back to the reservoir.
Key components of an overflow valve block include the valve itself, ports, and the body. It can be found in various applications, from construction machinery to industrial equipment. The design often includes a spring mechanism that ensures quick response. When pressure is normal, the valve remains closed, ensuring optimal performance.
However, these systems are not flawless. Over time, wear and tear can affect their responsiveness. Dirt or debris can clog the valve, leading to failure. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure efficiency. Remember, even small issues can lead to larger problems over time.
The Purpose and Importance of Overflow Valve Blocks
Overflow valve blocks play a critical role in hydraulic systems. They prevent excessive pressure buildup. When pressure exceeds a set limit, the valve opens. This allows excess fluid to escape, ensuring system safety. Without it, components can suffer from damage. Pressure fluctuations may lead to system failures.
The design of overflow valve blocks can vary, but their purpose remains consistent. They are vital for maintaining operational efficiency. These valves help prevent unnecessary wear and tear on machinery. However, if improperly calibrated or maintained, they may fail to protect the system. This can create costly repairs. Regular inspections are essential to ensure functionality.
In real-world applications, the stakes are high. A malfunctioning overflow valve can lead to catastrophic scenarios. Operators should be cautious and attentive. It’s important to reflect on the performance of these valves periodically. This proactive approach can prevent avoidable accidents. Understanding the purpose of overflow valve blocks is crucial for reliable system operation.
What Is an Overflow Valve Block and How Does It Work?
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Controls pressure and flow in hydraulic systems. |
| Applications | Used in construction, automotive, and manufacturing machinery. |
| Components | Typically includes a valve, spring, and adjustment mechanisms. |
| Operation Principle | Prevents system overpressure by bypassing fluid when pressure exceeds set limits. |
| Importance | Enhances safety and reliability of hydraulic systems by preventing damage. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections are recommended to ensure proper function. |
How Overflow Valve Blocks Function Mechanically
Overflow valve blocks play a crucial role in hydraulic systems. These blocks help maintain a desired pressure by diverting excess fluid. When pressure exceeds a set limit, the valve opens, releasing the fluid back into the reservoir. This action prevents pressure spikes, which can damage components.
Mechanically, overflow valve blocks consist of several parts. They usually include a spring, a valve seat, and a body. The spring applies pressure on the valve to keep it closed. Once the pressure in the system surpasses the threshold, the spring compresses, allowing the valve to open. According to industry reports, effective overflow valve functioning can improve system efficiency by up to 20%. Such improvements contribute to lower operational costs.
Tips: Regular maintenance of overflow valve blocks is essential. Check for leaks or wear on seals. This can prevent unexpected failures. Also, understanding how your specific system operates can help tailor the settings of the overflow valve block. Be aware that improper adjustments can lead to inefficient functioning.
Common Applications of Overflow Valve Blocks
Overflow valve blocks are essential in fluid systems. They prevent system pressure from exceeding safe levels. These blocks play a vital role in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Their primary function is to control fluid flow and pressure.
Common applications of overflow valve blocks include industrial machinery and automotive systems. In manufacturing, they ensure hydraulic presses operate safely. Without these valves, excessive pressure can damage equipment. In vehicles, they help maintain optimal braking systems. A malfunction in this area could lead to failure, posing safety risks.
Overflow valve blocks also find use in construction equipment. They help manage the hydraulic systems that lift heavy loads. Another application is in fluid transport systems. Here, they protect components from damage due to pressure surges. However, maintaining these valves requires attention. Issues like clogging can occur, leading to inefficient operation. Regular checks can prevent potential breakdowns.
Common Applications of Overflow Valve Blocks
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Overflow Valve Blocks
Maintaining an overflow valve block is crucial for systems that rely on hydraulic components. Regular maintenance helps avoid system failures. A study by the Fluid Power Association reveals that improper maintenance can lead to 30% efficiency loss in hydraulic systems. Scheduled inspections should be planned every six months. Check for leaks, blockages, and wear. Small issues can escalate quickly, leading to costly repairs.
Troubleshooting common problems is vital. For example, if an overflow valve isn't functioning, check the spool and spring. They must be clean and undamaged. Reports indicate that debris can cause 25% of valve malfunctions. It doesn't take much for a small fragment to disrupt flow. Regular cleaning can prevent this. Additionally, monitor temperature and pressure consistently. Any anomaly could indicate an underlying issue. Immediate action can save time and resources later.
